Tropical Plant Research
An International Journal by Society for Tropical Plant Research
2018, VOLUME 5 ISSUE 2Pages: 180-192
Exploring the potential of some phytodyes as histological stains in wood anatomy
A. J. Akinloye* and H. C. Illoh
*Botany Department, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Osun State, Nigeria
Abstract:
The potential of some phytodyes were examined to obtain cheap, non- toxic and eco-friendly stains for use in wood anatomy. Phytodyes from Enantia cholorantha, Harunganmadagascariensis, Hisbiscus sabdariffa, Sarcocephalus latifolius, Sphenocentrum jollyanum, and Sorghum bicolor were used to stain wood sections and macerates. All the extracts had good affinity for wood fibre and other lignified tissues except Hibiscus sabdariffa. The results of the absorption spectrum of these dyes revealed a range of wavelength of absorption between 300.00 and 900.00 nm. These wavelengths fall within the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum confirming the presence of colour imparting chromophores in the dyes. Each of the phytodye has minimum of two peaks, indicating that each dye had a minimum of two colour imparting chromophores. All the dyes were acidic with pH range of 2.80 to 5.90. The histochemical reactions of all the phytodyes were similar in that they all imparted their colours indiscriminately on all cells but fibre and lignified tissues took up the dyes more deeply. They were specific when used with Alican blue which have affinity for thin walled cells. Therefore, this study revealed that these dyes could be used solitarily or in combination with artificial dyes for wood histological staining.
The potential of some phytodyes were examined to obtain cheap, non- toxic and eco-friendly stains for use in wood anatomy. Phytodyes from Enantia cholorantha, Harunganmadagascariensis, Hisbiscus sabdariffa, Sarcocephalus latifolius, Sphenocentrum jollyanum, and Sorghum bicolor were used to stain wood sections and macerates. All the extracts had good affinity for wood fibre and other lignified tissues except Hibiscus sabdariffa. The results of the absorption spectrum of these dyes revealed a range of wavelength of absorption between 300.00 and 900.00 nm. These wavelengths fall within the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum confirming the presence of colour imparting chromophores in the dyes. Each of the phytodye has minimum of two peaks, indicating that each dye had a minimum of two colour imparting chromophores. All the dyes were acidic with pH range of 2.80 to 5.90. The histochemical reactions of all the phytodyes were similar in that they all imparted their colours indiscriminately on all cells but fibre and lignified tissues took up the dyes more deeply. They were specific when used with Alican blue which have affinity for thin walled cells. Therefore, this study revealed that these dyes could be used solitarily or in combination with artificial dyes for wood histological staining.
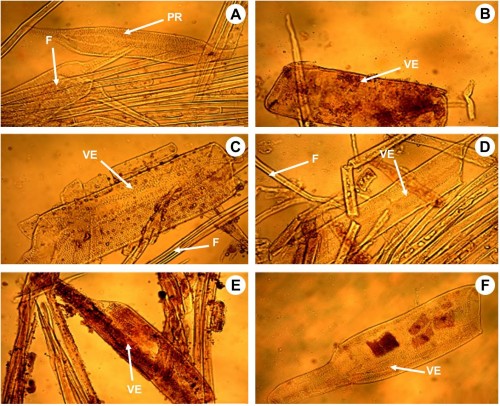
Fig.: Wood macerates of DiospyrospiscatoriaGürke(400x)
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 8 | 7 |


