Tropical Plant Research
An International Journal by Society for Tropical Plant Research
2018, VOLUME 5 ISSUE 3Pages: 286-291
Determination of nutrients and fiber contents of seven invasive plants and their decomposition rates
N. Hewavitharana*, S. D. P. Kannangara, L. R. Jayasekera and P. Weerasinghe
*Department of Botany, Faculty of Science, University of Kelaniya, Sri Lanka
Abstract:
Nutrients (C, N, P, K, Mg, Ca, Cu, Fe Mn and Zn), fiber contents and decomposition rates of seven invasive plants (Mikania scandens, Tithonia diversifolia, Lantana camara, Sphagneticola trilobata, Chromolaena odorata, Mimosa pigra and Panicum maximum) were analyzed aiming at their potentiality to prepare cost effective, organic compost for crop cultivation. Litter bag technique was used to measure the decomposition rates. Significantly the highest nutrient contents; N (3.44%), Mg (1.3%), Cu (34 mg kg-1), Fe (393 mg kg-1), Mn (150 mg kg-1) and Zn (671 mg kg-1) were found in M. scandens. T. diversifolia had significantly higher P (0.37%) and Ca (4.92%) contents than that of others. S. trilobata showed significantly higher K content (4.32%). Whereas, M. scandens and T. diversifolia showed significantly lower organic carbon contents (16.8% and 19.8%), crude fiber contents (4.85% and 3.50%) and C:N ratio (4.8 and 6.1) respectively. Significantly higher decomposition rates were observed in M. scandens (k= 12.91 per year) and T. diversifolia (k= 10.77 per year). Although the nutrient contents and decomposition rate (k= 3.41 per year) in P. maximum were significantly lower, but its carbon (33.7%), crude fiber content (20.42%) and C:N ratio (26.5) were significantly higher than that of others. T. diversifolia and M. scandens have the potential to use in low cost organic compost preparation, due to their comparatively higher nutrients and decomposition rates. P.maximum can also be incorporated in preparing compost for its higher crude fiber content to improve the soil physical properties.
Nutrients (C, N, P, K, Mg, Ca, Cu, Fe Mn and Zn), fiber contents and decomposition rates of seven invasive plants (Mikania scandens, Tithonia diversifolia, Lantana camara, Sphagneticola trilobata, Chromolaena odorata, Mimosa pigra and Panicum maximum) were analyzed aiming at their potentiality to prepare cost effective, organic compost for crop cultivation. Litter bag technique was used to measure the decomposition rates. Significantly the highest nutrient contents; N (3.44%), Mg (1.3%), Cu (34 mg kg-1), Fe (393 mg kg-1), Mn (150 mg kg-1) and Zn (671 mg kg-1) were found in M. scandens. T. diversifolia had significantly higher P (0.37%) and Ca (4.92%) contents than that of others. S. trilobata showed significantly higher K content (4.32%). Whereas, M. scandens and T. diversifolia showed significantly lower organic carbon contents (16.8% and 19.8%), crude fiber contents (4.85% and 3.50%) and C:N ratio (4.8 and 6.1) respectively. Significantly higher decomposition rates were observed in M. scandens (k= 12.91 per year) and T. diversifolia (k= 10.77 per year). Although the nutrient contents and decomposition rate (k= 3.41 per year) in P. maximum were significantly lower, but its carbon (33.7%), crude fiber content (20.42%) and C:N ratio (26.5) were significantly higher than that of others. T. diversifolia and M. scandens have the potential to use in low cost organic compost preparation, due to their comparatively higher nutrients and decomposition rates. P.maximum can also be incorporated in preparing compost for its higher crude fiber content to improve the soil physical properties.
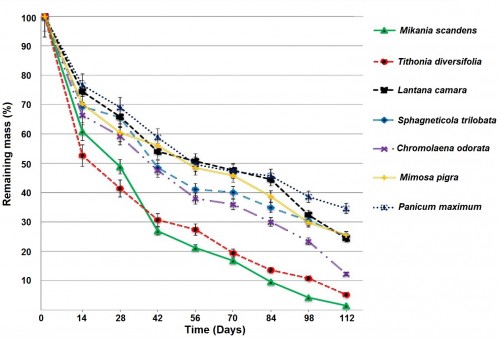
Fig.: Mean remaining mass (%) of invasive plants during decomposition period.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 0 |


