Tropical Plant Research
An International Journal by Society for Tropical Plant Research
2016, VOLUME 3 ISSUE 1Pages: 243-248
Variation in rock phosphate solubilization by three isolates of Aspergillus niger van Tieghem grown in liquid media supplemented with different carbon and nitrogen sources
Hruda Ranjan Sahoo and Nibha Gupta*
Abstract:
In the present study, we worked out the phosphate solubilization potential of three different isolates of Aspergillus niger from various sources such as leaf (L), root (R) and soil (S) under different carbon and nitrogen supplementation in liquid culture. The fungal cultures were inoculated in Czapek Dox Medium containing different carbon and nitrogen sources and supplemented with Moroccan rock phosphate. The fungal strains exhibited good potential favoring the solubilization of rock phosphate in laboratory conditions. On carbon sources modification, Aspergillus niger (L) and (S) showed highest P solubilization activity 27.6% and 29.6% respectively in presence of glucose whereas Aspergillus niger (R) showed highest P solubilization of 27.8% in presence of inositol. Similarly on modification of nitrogen sources, Aspergillus niger (L) and (S) showed maximum solubilization of 35.25% and 40.8% respectively, but Aspergillus niger (R) showed maximum solubilization of 37% in presence of amino acid L-phenylalanine in culture broth. Further pot experiment with different soil composition and host plants may exhibit its exploitable potential.
In the present study, we worked out the phosphate solubilization potential of three different isolates of Aspergillus niger from various sources such as leaf (L), root (R) and soil (S) under different carbon and nitrogen supplementation in liquid culture. The fungal cultures were inoculated in Czapek Dox Medium containing different carbon and nitrogen sources and supplemented with Moroccan rock phosphate. The fungal strains exhibited good potential favoring the solubilization of rock phosphate in laboratory conditions. On carbon sources modification, Aspergillus niger (L) and (S) showed highest P solubilization activity 27.6% and 29.6% respectively in presence of glucose whereas Aspergillus niger (R) showed highest P solubilization of 27.8% in presence of inositol. Similarly on modification of nitrogen sources, Aspergillus niger (L) and (S) showed maximum solubilization of 35.25% and 40.8% respectively, but Aspergillus niger (R) showed maximum solubilization of 37% in presence of amino acid L-phenylalanine in culture broth. Further pot experiment with different soil composition and host plants may exhibit its exploitable potential.
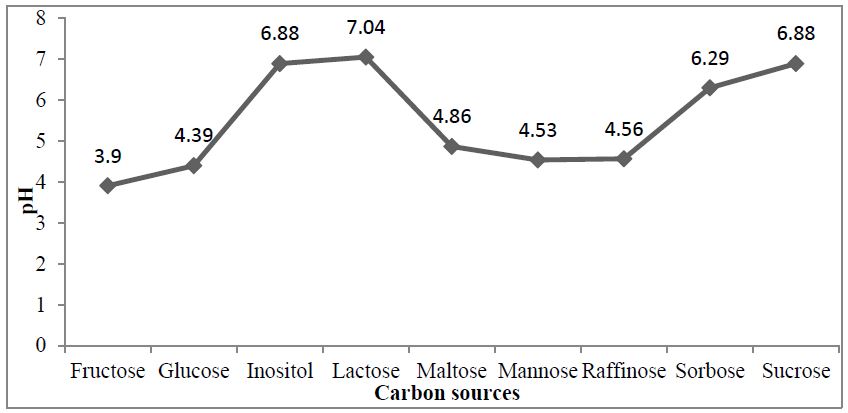
Fig.: Effect of carbon sources on pH drift during P solubilisation in Aspergillus niger
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 0 |


